Let us see how to use the NTFS disk compression to save disk space on Windows PC.
How to Free up Disk Space on Windows
NTFS stands for New Technology File System, although this file system was introduced with Windows NT and is not really new anymore. It is, however, the default file system that Windows uses. It comes with a built-in compression technology that allows you to compress files, without having to zip them up in an archive. Using NTFS file compression on Windows is rather simple. I can, however, take quite a lot of time to complete the process, depending on the size of your drive and the number and type of files on it. Windows will then begin to compress the entire drive and as mentioned before, this can take a while. The amount of time this takes will depend on the number of files, their sizes, and type as well as the speed of your hard disk or SSD.
How Much Space Does NTFS Compression Save?
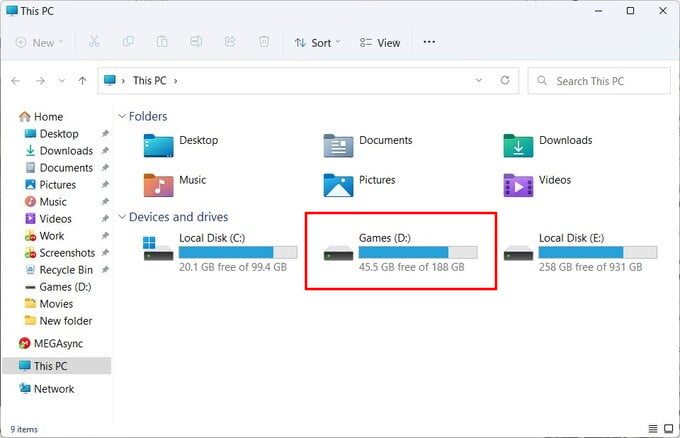
The amount of disk space you can free up with NTFS compression will also depend on the types of files on the drive. If you have a bunch of zip files on the drive, for instance, compression will not result in much difference. Similarly, video files don’t compress too much. Text files, on the other hand, can be compressed very efficiently. For example, we used Compress this drive to save disk space on a drive with a bunch of installed games. As you can see in the screenshots, the results are significant and quite worth it. When there was only 31.5 GB of free space on the drive before compression, it now has 45.5 GB of free space after compression. Unfortunately, there’s really no other way to see how much space you will save unless you actually enable the feature.
Does NTFS Compression Slow Down Your Computer?
As with all things, there are pros and cons to this as well. NTFS compression has the advantage of keeping all your files accessible, instead of zipping them into an archive. However, these are still compressed files. This means that they need to be decompressed every time they are to be used. That requires some resources on the computer’s part. Again, there are no ironclad numbers on just how much of a performance cost you’d have to pay. Generally, this depends on the processor. If your device has a fast processor, you will not even notice any difference. In fact, in the case of a fast processor but a slower hard disk, you might even see a performance improvement in reading the file. That’s because the hard drive is slower, so it is faster for it to read a smaller, compressed file compared to a larger file. Also, keep in mind that all the compressing and decompressing results in more read and write cycles overall. This may not be beneficial for an SSD in the long run. However, if you have a small size SSD, this can save you significant space.
When Should You Use NTFS Compression on Windows Disk?
NTFS compression is definitely worth it, but not for everyone. If you have a large drive with a ton of free space, there’s really no point in trying to save a few GB of space when the method does have some downsides. For people with a small drive, those few GBs of space can be a huge difference. Then again, if your CPU is already slow, this will slow it down even further. Users with a small drive with slower speeds and faster CPU speeds are sure to see the most benefits.
Δ